pyblenderSDIC.meshes.create_xy_heightmap_mesh#
- create_xy_heightmap_mesh(height_function: ~typing.Callable[[float, float], float] = <function <lambda>>, frame: ~py3dframe.frame.Frame = Frame(origin=[[0.] [0.] [0.]], x_axis=[[1.] [0.] [0.]], y_axis=[[0.] [1.] [0.]], z_axis=[[0.] [0.] [1.]], x_bounds: tuple[float, float] = (-1.0, 1.0), y_bounds: tuple[float, float] = (-1.0, 1.0), Nx: int = 10, Ny: int = 10, first_diagonal: bool = True, direct: bool = True, uv_layout: int = 0) TriangleMesh3D[source]#
Create a 3D XY-plane mesh with variable height defined by a surface function.
The surface is defined by a function that takes two arguments (x and y) and returns a scalar height z. The returned value is interpreted as the vertical position of the surface at that point.
The
frameparameter defines the orientation and the position of the mesh in 3D space. The (x, y) grid is centered on the frame origin, lying in the local XY plane. The height (z) is applied along the local Z-axis of the frame.The
x_boundsandy_boundsparameters define the rectangular domain over which the mesh is generated.NxandNydetermine the number of vertices along the x and y directions, respectively. Nodes are uniformly distributed across both directions.Note
NxandNyrefer to the number of vertices, not segments.The height function must return a finite scalar value for every (x, y) in the specified domain.
For example, the following code generates a sinusoidal surface mesh centered on the world origin:
from pyblenderSDIC.meshes import create_xy_heightmap_mesh import numpy as np surface_mesh = create_xy_heightmap_mesh( height_function=lambda x, y: 0.5 * np.sin(np.pi * x) * np.cos(np.pi * y), x_bounds=(-1.0, 1.0), y_bounds=(-1.0, 1.0), Nx=50, Ny=50, ) surface_mesh.visualize()
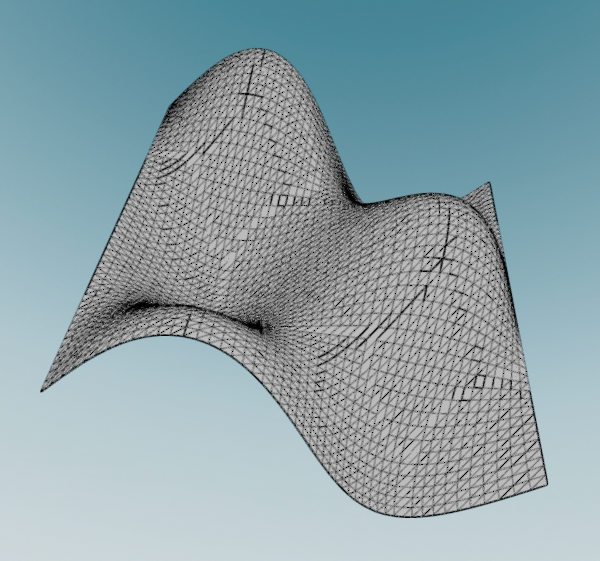
Sinusoidal height map over a square domain centered at the origin.#
Nodes are ordered first in y (indexed by
i_Y), then in x (indexed byi_X). So the vertex at y indexi_Yand x indexi_X(both starting from 0) is located at:mesh.vertices[i_Y * Nx + i_X, :]
Each quadrilateral face is defined by the vertices:
\((i_X, i_Y)\)
\((i_X + 1, i_Y)\)
\((i_X + 1, i_Y + 1)\)
\((i_X, i_Y + 1)\)
This quadrilateral is split into two triangles depending on the value of
first_diagonal:If
first_diagonalisTrue:Triangle 1: \((i_X, i_Y)\), \((i_X, i_Y + 1)\), \((i_X + 1, i_Y + 1)\)
Triangle 2: \((i_X, i_Y)\), \((i_X + 1, i_Y + 1)\), \((i_X + 1, i_Y)\)
If
first_diagonalisFalse:Triangle 1: \((i_X, i_Y)\), \((i_X, i_Y + 1)\), \((i_X + 1, i_Y)\)
Triangle 2: \((i_X, i_Y + 1)\), \((i_X + 1, i_Y + 1)\), \((i_X + 1, i_Y)\)
By default, the triangles are oriented counterclockwise (direct orientation) for an observer looking from above. Set
direct=Falseto reverse the orientation.The UV coordinates are generated based on the vertex positions in the mesh and uniformly distributed in the range [0, 1] for the OpenGL texture mapping convention. Several UV mapping strategies are available and synthesized in the
uv_layoutparameter. The following options are available foruv_layout:uv_layout
Vertex lower-left corner
Vertex upper-left corner
Vertex lower-right corner
Vertex upper-right corner
0
(0, 0)
(Nx-1, 0)
(0, Ny-1)
(Nx-1, Ny-1)
1
(0, 0)
(0, Ny-1)
(Nx-1, 0)
(Nx-1, Ny-1)
2
(Nx-1, 0)
(0, 0)
(Nx-1, Ny-1)
(0, Ny-1)
3
(0, Ny-1)
(0, 0)
(Nx-1, Ny-1)
(Nx-1, 0)
4
(0, Ny-1)
(Nx-1, Ny-1)
(0, 0)
(Nx-1, 0)
5
(Nx-1, 0)
(Nx-1, Ny-1)
(0, 0)
(0, Ny-1)
6
(Nx-1, Ny-1)
(0, Ny-1)
(Nx-1, 0)
(0, 0)
7
(Nx-1, Ny-1)
(Nx-1, 0)
(0, Ny-1)
(0, 0)
The table above gives for the 4 corners of a image the corresponding vertex in the mesh.
See also
pyblenderSDIC.meshes.TriangleMesh3Dfor more information on how to visualize and manipulate the mesh.Artezaru/py3dframe for details on the
Frameclass.
- Parameters:
height_function (Callable[[float, float], float]) – A function that takes x and y coordinates and returns the corresponding height (z).
frame (Frame, optional) – The reference frame for the mesh. Defaults to the identity frame.
x_bounds (tuple[float, float], optional) – The lower and upper bounds for the x coordinate. Default is (-1.0, 1.0).
y_bounds (tuple[float, float], optional) – The lower and upper bounds for the y coordinate. Default is (-1.0, 1.0).
Nx (int, optional) – Number of vertices along the x direction. Must be more than 1. Default is 10.
Ny (int, optional) – Number of vertices along the y direction. Must be more than 1. Default is 10.
first_diagonal (bool, optional) – If True, the quad is split along the first diagonal (bottom-left to top-right). Default is True.
direct (bool, optional) – If True, triangle vertices are ordered counterclockwise. Default is True.
uv_layout (int, optional) – The UV mapping strategy. Default is 0.
- Returns:
The generated surface mesh as a TriangleMesh3D object.
- Return type: